AIreflections#7 - transformer architecture
Let us take a deep dive into the transformer architecture - key to the recent success of large language models.
The transformer architecture, introduced in the seminal 2017 paper “Attention is All You Need” [2], has revolutionized natural language processing and is the foundation of state-of-the-art large language models like GPT-3, PaLM, and others [1] [10]. The key innovation of the transformer is relying entirely on self-attention mechanisms to compute representations of input and output sequences, dispensing with recurrent and convolutional neural networks used in prior architectures [2] [14].
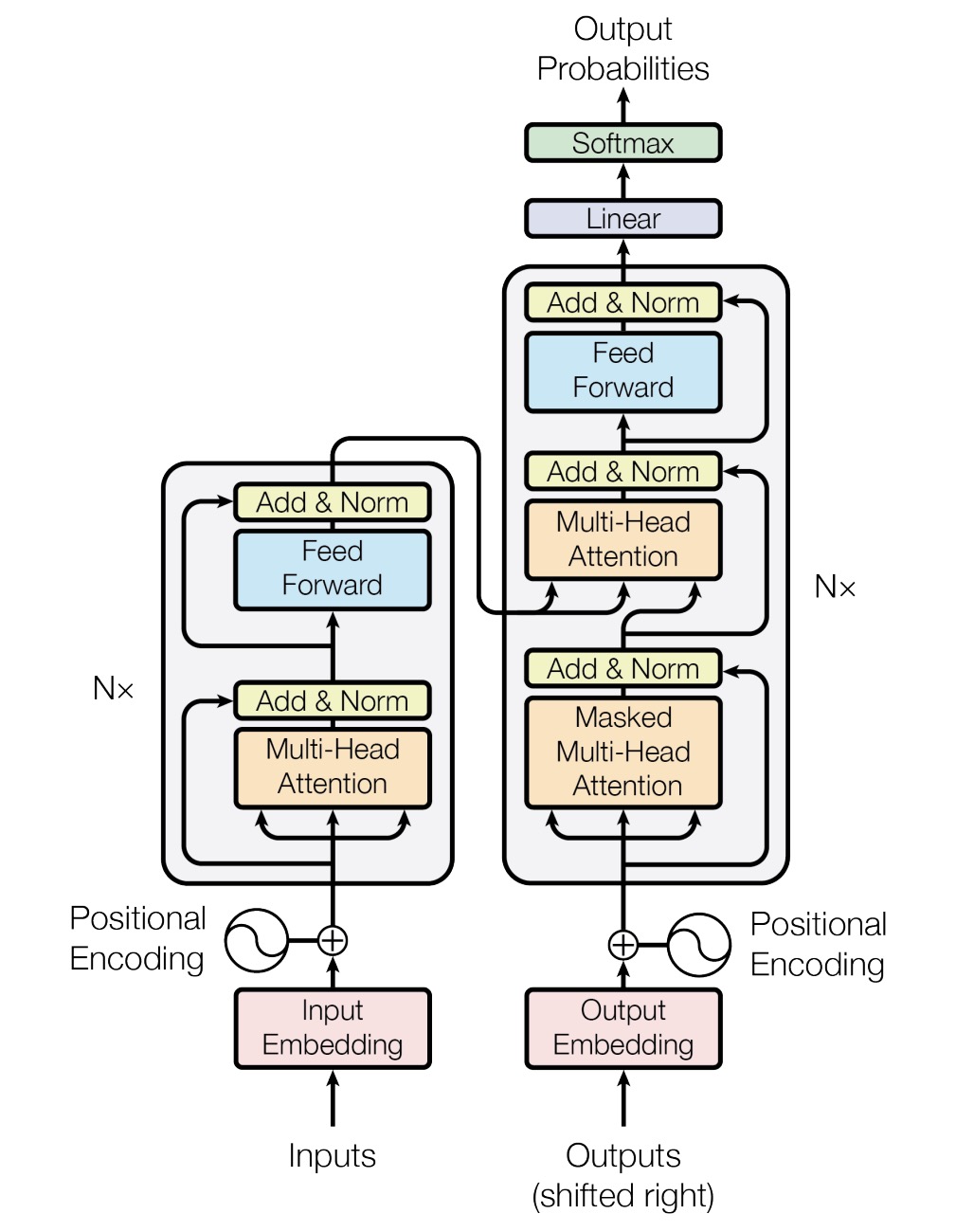
The transformer uses an encoder-decoder structure, with the encoder mapping an input sequence to a sequence of continuous representations, and the decoder generating an output sequence one element at a time [2] [17]. Both the encoder and decoder are composed of stacks of identical layers. Each encoder layer has two sub-layers: a multi-head self-attention mechanism and a position-wise fully connected feed-forward network. Each decoder layer has an additional third sub-layer performing multi-head attention over the encoder output [2] [15].
The self-attention mechanism is the core of the transformer, allowing the model to attend to different positions of the input sequence to compute a representation [2] [14]. In self-attention, three vectors - a query, key, and value - are created from each of the encoder’s input vectors (the embeddings of each input element like a word) [17]. The output is a weighted sum of the values, where the weights are determined by the compatibility of the query with the corresponding key [14] [17].
Multi-head attention performs multiple self-attention operations in parallel, allowing the model to jointly attend to information at different positions from different representational spaces [2] [14]. The outputs are concatenated and linearly transformed into the expected dimensions.
Since the transformer contains no recurrence, positional encodings are added to the input embeddings to inject information about the position of elements in the sequence [1] [2]. This can be done through fixed positional encodings using sine and cosine functions of different frequencies [2] [8], or learned positional embeddings [11] [18].
The transformer leverages residual connections around each sub-layer and layer normalization after each sub-layer [2] [15]. The feed-forward networks contain two linear transformations with a ReLU activation in between.
The transformer’s attention mechanisms allow it to effectively capture long-range dependencies and parallelize computations, significantly speeding up training [3] [16]. Stacking multiple attention layers increases the receptive field, allowing the network to learn more complex relationships [15].
The transformer architecture, with its self-attention, multi-head attention, positional encodings, residual connections, and feed-forward layers, has become the backbone of large language models [12]. Its ability to attend to all positions in the input, integrate information effectively, and parallelize has enabled training on massive amounts of data to create powerful LLMs that excel at language understanding and generation tasks [1] [10] [13]. Ongoing research continues to build on the transformer to make LLMs more capable, efficient and aligned to human values.
In summary, the transformer architecture and its attention mechanisms have been instrumental in unlocking the potential of large language models. Its elegant yet powerful design has ushered in a new era of natural language processing and continues to be the foundation for rapid advances in LLMs.
References
[1] gopenai.com: Unleashing the Power of Position: Positional Encoding in Transformers
[2] neurips.cc: Attention Is All You Need
[3] datagen.tech: What Is the Transformer Architecture and How Does It Work?
[4] reddit.com: How Does Self-Attention Work in Transformer Models?
[5] arxiv.org: Transformer-Based Architectures for Large Language Models: A Survey
[6] frontiersin.org: Transformer-Based Language Models: A Survey
[7] aimultiple.com: Large Language Models (LLMs): The Complete Guide
[8] machinelearningmastery.com: A Gentle Introduction to Positional Encoding in Transformer Models
[9] towardsdatascience.com: Understanding Positional Encoding in Transformers
[10] uctoday.com: The Best Large Language Models in 2023
[11] linkedin.com: Deep Dive into Positional Encodings in Transformer Neural Network
[12] arxiv.org: Transformer-Based Architectures for Large Language Models: A Survey
[13] hostinger.com: What Are Large Language Models? The Complete Guide
[14] machinelearningmastery.com: The Transformer Attention Mechanism
[15] jeremyjordan.me: Transformer Architecture: The Positional Encoding
[16] towardsdatascience.com: Attention and Transformer Models
[17] jalammar.github.io: The Illustrated Transformer
[18] reddit.com: Why is Positional Encoding Learned in Vision Transformers?
[19] datascience.stackexchange.com: What is the Positional Encoding in the Transformer Model?
[20] paperspace.com: Learning in Latent Spaces Improves the Predictive Accuracy of Deep Neural Operators
Based on a chat with claude-3-opus on perplexity.ai
